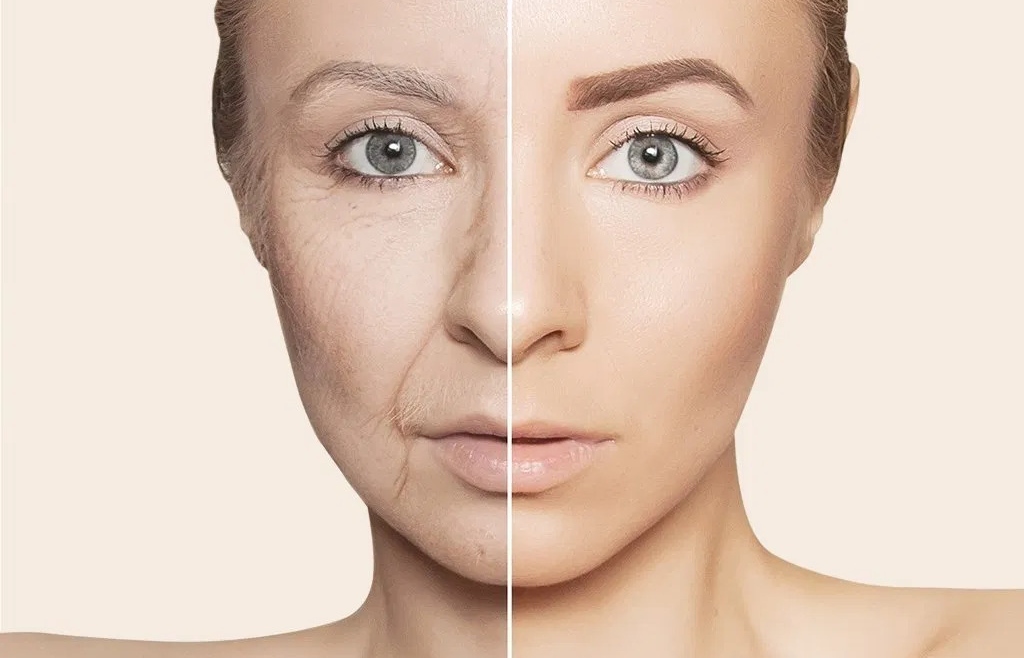
Being the outermost cover of the body, the skin remains completely exposed to the environment and is vulnerable to injuries. This is compounded by the wear and tear of skin cells due to aging, natural bodily changes, or other medical conditions. Healthy skin is fully capable of repairing itself through a cycle of skin cell regeneration. Every day, people shed thousands of dead skin cells without even realizing it, and fresh new skin cells form in their place. However, this cycle tends to slow down with advancing age and can get further disrupted by other adverse factors. This then leads to wrinkles, fine lines, and gradual loss of skin elasticity.
Elasticity refers to the ability of the skin to stretch and then return to its original shape without getting loose. Thus, the less elastic the skin, the more it will sag. Saggy skin is one of the prime indicators of skin aging, but it can be a result of other factors as well, which will be discussed in this article.
Causes of skin sagging include:
- Genetics
- Ethnicity
- Medical conditions, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Pregnancy
Causes of skin sagging are:
- Prolonged exposure to the UV rays of the sun
- Air pollution
- Smoking
- Poor nutrition
- Inadequate hydration
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Sudden and rapid weight loss, such as after a bariatric surgery
Symptoms of Saggy Skin
Loose skin is not a medical condition itself, but a sign of skin aging or other forms of skin damage. The areas most prone to skin sagging are your stomach, face, neck, arms, legs, and hips. Flappy, hanging skin is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Fine lines and wrinkles, especially on the face
- Loss of skin color, which makes it look increasingly pale or pigmented
- Increased skin sensitivity